A closer look at Evilginx and how MFA doesn’t protect against this modern phishing technique.
Staying ahead of cybersecurity threats is crucial, and one of the latest to emerge is Evilginx. This sophisticated phishing technique imposes significant risks even to the most secure accounts with MFA. This article explores what Evilginx is, the dangers it presents, and effective strategies for safeguarding yourself against this advanced phishing tool. The primary concern with Evilginx is its ability to circumvent 2FA, a security measure that has become a standard defence against unauthorized access.
What is Evilginx?
Evilginx is the newest iteration in a series of advanced phishing tools that act as “man-in-the-middle” attackers. It intercepts communications between a user and legitimate websites, stealthily capturing login credentials and even bypassing two-factor authentication (2FA). This tool can mimic interactions with well-known platforms, making it challenging to detect and defend against. To truly grasp how Evilginx operates, it’s crucial to understand what a “token” is in the context of online authentication.
In simple terms, a token in online security is like a temporary digital key. When you log in to a website, even with two-factor authentication (2FA), the website generates a unique, one-time-use token. This token verifies that you’ve successfully passed the login challenge (like entering a correct password and a 2FA code). Instead of keeping your password and 2FA code active for the session, the website uses this token to remember that you’ve been authenticated. It’s a way to keep your session secure without constantly sending your sensitive information back and forth. This token is stored on your local computer.
By capturing session tokens (also known as cookies), Evilginx enables attackers to access accounts as if they were legitimate owners, leading to potential data breaches, identity theft, and financial loss. This tool’s effectiveness significantly raises the stakes in the ongoing battle against phishing attacks.
Example Attack Scenario
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of what happens during an Evilginx attack:
- Phishing Stage: You receive an incredibly legitimate looking email directing you to log in to a website (say, Microsoft 365)
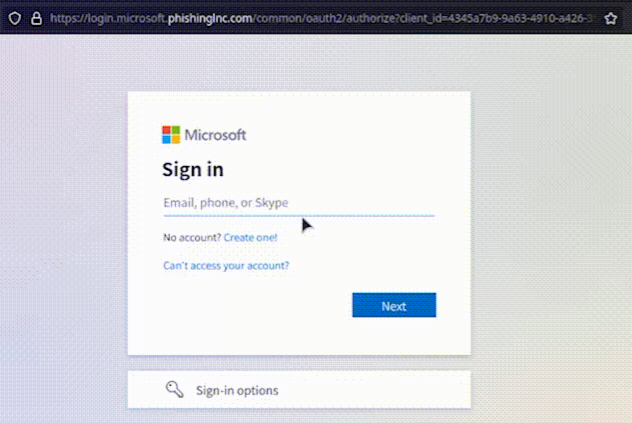
- The Fake Login Page: The link in the email redirects you to a malicious site that is almost a perfect replica of the real site. This site is delivered by Evilginx, sitting quietly between you and the actual service provider’s website.
- Data Interception: When you enter your login credentials and 2FA code, Evilginx captures them. But it doesn’t stop there. It also intercepts the token issued by the real website once you’ve authenticated successfully.
- Session Hijacking: With your credentials, 2FA code, and the token, the attacker can now access your account. The token is especially valuable because it grants them access without needing to re-enter the 2FA code, effectively bypassing this security measure.
- Unauthorized Access: Armed with the token, the attacker can do anything from stealing personal information to making transactions, all while impersonating you.
How to Safeguard Against Token Theft
Protecting yourself from such a nuanced threat involves a multifaceted approach:
- Stay Skeptical: Treat unexpected emails with caution, especially those prompting you to log in or verify your account details.
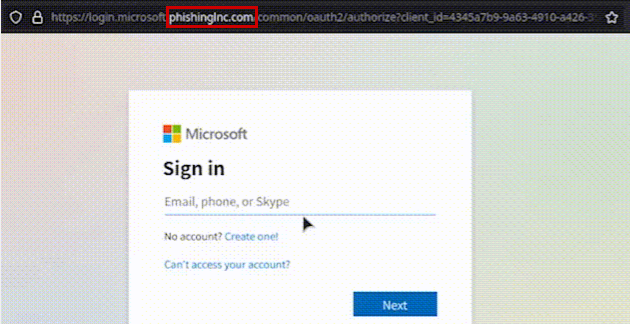
- Review the URL you are visiting:
 https://login.microsoft.phishingInc.com/
https://login.microsoft.phishingInc.com/
Why? “phishingInc.com” is clearly NOT a Microsoft website. - Assume all links provided in e-mails are hostile. Visit the company’s website directly and use the URLs they provide on their own website (don’t use what’s included in the e-mail or text message).
- Assume all attachments received from a third party or links within these attachments are hostile. Contact the sender to verify BEFORE you open anything.
- For any large change requests sent by e-mail, especially billing related, call the other party to verify in case their mailbox was compromised
- Use External Sender warnings to notify recipients that the sender is not from your team
- Separate administrator accounts (admin@you.onmicrosoft.com) from operational accounts (john@yourdomain.com)
- Were you expecting an email? Call the sender and ensure they meant to send it.
- Ask your IT department to verify!
- Review the URL you are visiting:
- Use Cloud-Based Monitoring Tools: Employ comprehensive security solutions that can detect abnormal behaviour in a cloud environment or help identify phishing attempts and malicious websites.
- Educate Continuously: Regularly test your team by sending phishing campaigns and monitoring the results. Train Train Train! Cybersecurity education can dramatically reduce the risk of falling for phishing schemes.
Other Considerations
- Setting up and using Evilginx is very easy and doesn’t take a lot of time or experience. Therefore, all businesses of all sizes are at risk.
- Many vendors are potentially at risk including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Amazon, Netflix, LinkedIn, etc. Anyone online.
In Conclusion
Evilginx showcases the sophistication of modern cyber threats, underlining the importance of being vigilant and informed. Understanding how your data, including tokens, can be compromised is the first step in fortifying your defences. By implementing robust security measures and fostering an environment of cybersecurity awareness, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to such advanced phishing attacks.
Remember, in the digital realm, knowledge is not just power—it’s protection.
If you’d like to chat with us about our Managed IT & Security Services, please don’t hesitate to reach out.